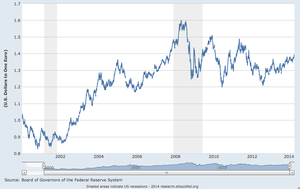
 (click to enlarge)
(click to enlarge) Monetary policy is the avenue through which governments can control the supply of money in the economy in order to stimulate growth. Expansionary policy is instituted to control unemployment during recessionary periods. The idea is to lower interest rates and make credit available so that businesses will expand.
Often inflation is described as too much money chasing too few goods. Prices of goods seem to be moving at lightening speed. Some inflation is good, it represents economic growth. When there is too much inflation in the economy, a monetary policy of contraction is established in an attempt to curb the erosion of asset values. Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy. Fiscal policy attempts to stimulate the economy through taxation, government spending and associated borrowing.
The US economy has been under Quantitative Easing (QE) for the past several years. We have been through QE1, QE2 and QE3 all various forms of the Federal Reserve's attempt to stimulate the economy. Other central banks around the world have implemented various forms of quantitative easing. The idea is to buy a specified amount of financial assets from commercial banks and other private institutions. This increases the monetary base and lowers the yield on those assets.
Often inflation is described as too much money chasing too few goods. Prices of goods seem to be moving at lightening speed. Some inflation is good, it represents economic growth. When there is too much inflation in the economy, a monetary policy of contraction is established in an attempt to curb the erosion of asset values. Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy. Fiscal policy attempts to stimulate the economy through taxation, government spending and associated borrowing.
The US economy has been under Quantitative Easing (QE) for the past several years. We have been through QE1, QE2 and QE3 all various forms of the Federal Reserve's attempt to stimulate the economy. Other central banks around the world have implemented various forms of quantitative easing. The idea is to buy a specified amount of financial assets from commercial banks and other private institutions. This increases the monetary base and lowers the yield on those assets.
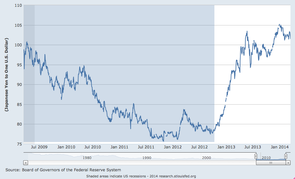 (click to enlarge)
(click to enlarge) One of the big trends we expect in 2014 is the divergence in monetary policy among the major central banks. The UK, Canada and Australia all have an easy stance. Japan is super easy, and the Fed is becoming less easy. But Europe still has a tight monetary policy even though policymakers there continue to talk about doing "whatever it takes." Consensus is that the European Central Bank (ECB) will need to relent and embrace quantitative easing because the credit crunch is worsening.
If monetary policy divergences continue, the euro could fall, and combined with a downtrend in the Japanese yen, on a trade-weighted basis, that would push the U.S. dollar higher. A stronger dollar typically makes exports less competitive, leads to lower inflation and attracts foreign capital to the bond market, helping to hold down interest rates. The euro came into 2014 on a firm note, indicating that the foreign exchange market is not convinced the ECB will change its policies. A reversal could signal perceptions that policies have changed. Do you favor a strong dollar? Sua Sponte
Bradford C. Bruner for Sua Sponte Wealth Management
If monetary policy divergences continue, the euro could fall, and combined with a downtrend in the Japanese yen, on a trade-weighted basis, that would push the U.S. dollar higher. A stronger dollar typically makes exports less competitive, leads to lower inflation and attracts foreign capital to the bond market, helping to hold down interest rates. The euro came into 2014 on a firm note, indicating that the foreign exchange market is not convinced the ECB will change its policies. A reversal could signal perceptions that policies have changed. Do you favor a strong dollar? Sua Sponte
Bradford C. Bruner for Sua Sponte Wealth Management